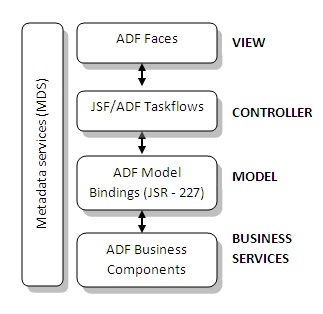
In this post I’ll list down the tools and set ups required to start building ADF Applications.
We will be using the Oracle JDeveloper as IDE and Oracle 10g XE as our database in all our further developments. All Oracle products are free to download and use for individual learning purpose. You can download these products from Oracle site.
JDeveloper:
JDeveloper is an IDE which makes the life of a developer easy with visual editors. You can simply develop an application with very less coding or no coding at all! Go to the below link and download the latest 11g version of Jdeveloper studio edition.
Here are the system requirements for windows.
CPU Speed 2 GHz or faster
Memory 2 GB RAM
Disk Space 2.5 GB
JDK JDK 6.0 Update 11
Set the Environment variable JDEV_USER_DIR,
JDEV_USER_HOME to directory where you would like your source code to be placed. You can cross verify that variable is set by executing 'Set JDEV_USER_DIR' command in the command prompt. Oracle 10g Express Edition Database:
Oracle 10g XE is a light weight DB and occupies very less space in your system. You can download it from the below link.
During the install It’ll ask you to provide a default password for SYS and SYSTEM, provide a password and remember it. Once the installation is done go to command prompt and execute the following steps.
1. At command prompt type ‘sqlplus system’. It’ll then ask for password. Give the password you entered during the installation.
2. Type the following command in the SQL> prompt ‘alter user hr identified by hr account unlock;’ - this will unlock the HR schema.
3. Exit the command prompt.
The HR schema contains Employees, Departments, Jobs, Countries and other tables. We use these tables for our further excercises.
Now we have the IDE & DB ready, We can start the tutorials!