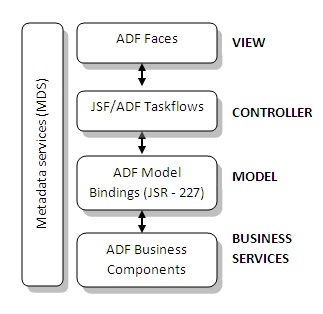
In this post we’ll go through the business services part of ADF architecture i.e., ADF business components (ADF BC). Let’s see what they can do, what all ADF BC consists and later how we develop them. We’ll also create sample ADF BC components.
In a typical application a developer have to take care of all the following when dealing with data.
-> Establishing a connection to database.
-> Retrieving data and buffering the data.
-> Locking the data for DML operations.
-> Managing the transactions across multi user environments.
Imagine with ADF BC libraries and JDeveloper you can do all these without writing a single piece of code!
Apart from those you can achieve the following with very less coding.
-> Build and enforce business logic across application at a single point.
-> Trim the database views to do only specific tasks.
-> You can simply modify and maintain the business functionality directly on ADF BC instead of modifying the already built application.
-> Provide updatable views from a desktop, mobile, browser and web service clients.
-> You can also verify and test all the business validations/functionality before you actually build the application.
To be simple, ADF BC is like a wrapper on top of the database which provides additional functionality.
ADF BC Components:
The following are the core business components.
1) Entity Objects (EO) – Represents a row in a database table. Entity objects hold the business validation logic and also handle DML operations. It can be built on a single table/ view / synonym.
2) View Objects (VO) – Represents a SQL query. They generally focus is on how we present data to client.
3) Application Module (AM) – Provides single point of access to all VO’s to achieve a task. Its job is to maintain all transactions.
Apart from the above we have Entity Associations and View Links. Entity associations are used to depict the relation between two Entity Objects (such as foreign key relation) just like the database tables are related. View Links represents the relations between two View Object result sets such as master detail relation.
Creating and testing ADF BC using wizard:
In this tutorial we create ADF BC components for Employee and Department tables using the wizard and do test them by performing DML operations through them.
Step 1: Start the Jdeveloper and choose ‘Default role’ when prompted.
Creating and testing ADF BC using wizard:
In this tutorial we create ADF BC components for Employee and Department tables using the wizard and do test them by performing DML operations through them.
Step 1: Start the Jdeveloper and choose ‘Default role’ when prompted.
Step 2: Select ‘New Application’, give application name as ‘ProjectADF’, Application Package Prefix as ‘sdadi.oracle.apps.hr’, select Fusion Web Application (ADF) as application template and click ‘Finish’.
The general naming convention is <com>.<your company>.<your app>.<your module> and sub packages if any.
Jdeveloper creates two projects ‘Model’ and ‘View Controller’. The model part deals with the ADF Business Components and ‘View Controller’ deals with UI and control parts of the application. In this tutorial we focus only on the Model.
Step 4: Select Business Tier > ADF Business Components >> Business Components From Tables and click OK.
Step 5: Click on the ‘+’ to create a new database connection. Provide the connection details (hr/hr) as in the figure. Verify connection details by clicking ‘Test Connection’. Click OK after verifying the connection is 'Success!'
I am assuming that oracle DB is already installed and HR schema is unlocked as given in the earlier post.
Step 6: Set the package as ‘sdadi.oracle.apps.hr.schema.server’. This is just to ensure that all the Entity objects are created under this folder. Set Name Filter to ‘%’ and Click on ‘Query’ to see all objects (Tables, Views and Synonyms) under HR schema.
Shuffle ‘Employees’ and ‘Departments’ and change the Entity names to EmployeeEO and DepartmentEO. This is just a naming convention for ease of use in future.
Step 7: Set the package as ‘sdadi.oracle.apps.hr.server’ and shuffle both the entity objects. Rename the view object names to EmployeeVO and DepartmentVO.
Step 8: We are not planning to create any read only view objects in this so just click on next. (Read Only view objects are similar to read only views in the DB, you cannot use them to do DML operations)
Step 10: All the required ADF business components are created automatically by JDeveloper and ready to use. You observe that the required Entity Associations and View Links are created based on the database constraints.
Step 11: Test the created ADF BC by right clicking on ‘EmpDeptAM’ > Run. This will open a window with all the view objects and view links included in the AM.
Step 12: You verify by double clicking the view objects and view links and see that rows are fetched accordingly. You can insert a record, delete a record, commit the database, modify a record or simply navigate between records.